(06/10/23) Blog 279 – Looney Tunables – that’s all folks!
A number of Proof-Of-Concept (PoC) exploits have surfaced on the Internet which target a high-severity flaw in a number of Linux distributions which give attackers Root privileges if sucessful.
The vulnerability is tracked as CVE-2023-4911 and relates to a buffer overflow issue which if exploited can give an attacker the ability to run arbitrary code with elevated privileges.
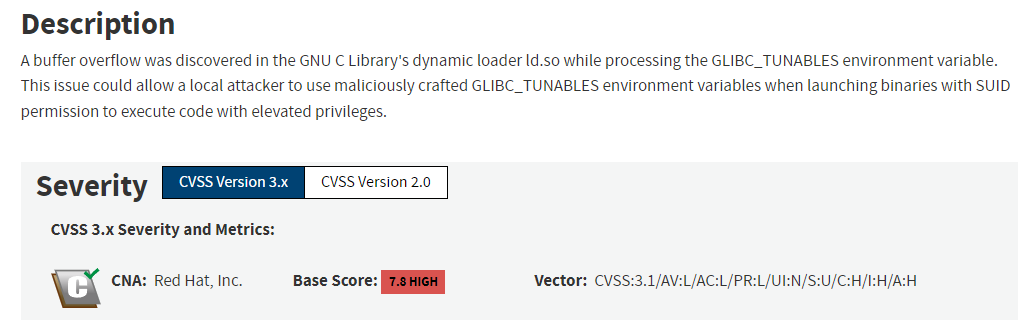
The vulnerability has been identified in many widely-used variants of Linux including Debian, Gentoo, Fedora, Redhat, and Openwall (OWL).
The naming of the vulnerability comes from the fact that if affects the C library’s dynamic loader ld.so when it processes the GLIBC_TUNABLES environment variable.
These tunables allow application authors and distribution maintainers to alter the runtime library behavior to match their workload – so for example, a developer could use the tunable to limit the size of data a specific executable could handle at any one time.
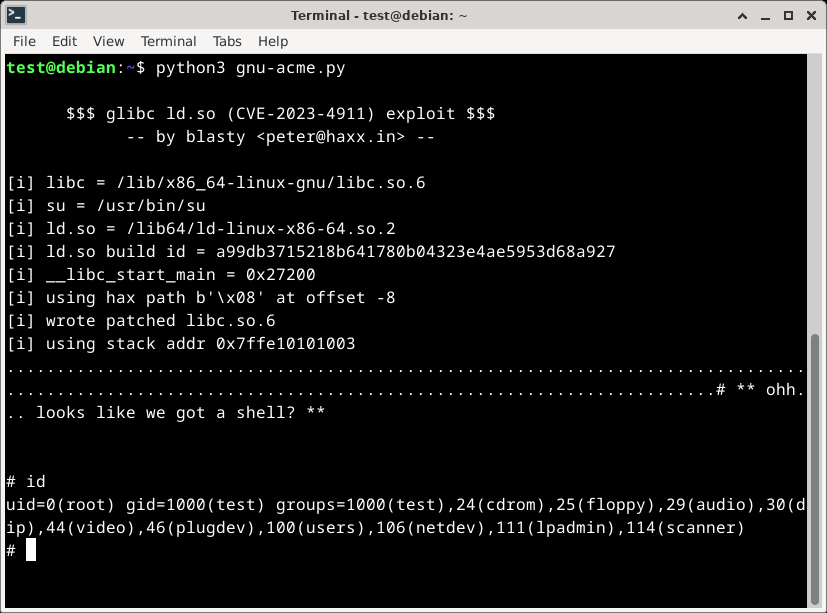
A full disclosure of the vulnerability was posted by the qualys threat research team on Tuesday (3rd Oct) and by Thursday morning a number of PoCs had been produced.
One of the first PoCs was released by security researcher Peter Geissler (@bl4sty) and was released as a python script
Until a permanent fix has been released, a number of Linux distro outlets have produced mitigation / workaround options which should be applied by sys admins as soon as possible to avoid exploitation.