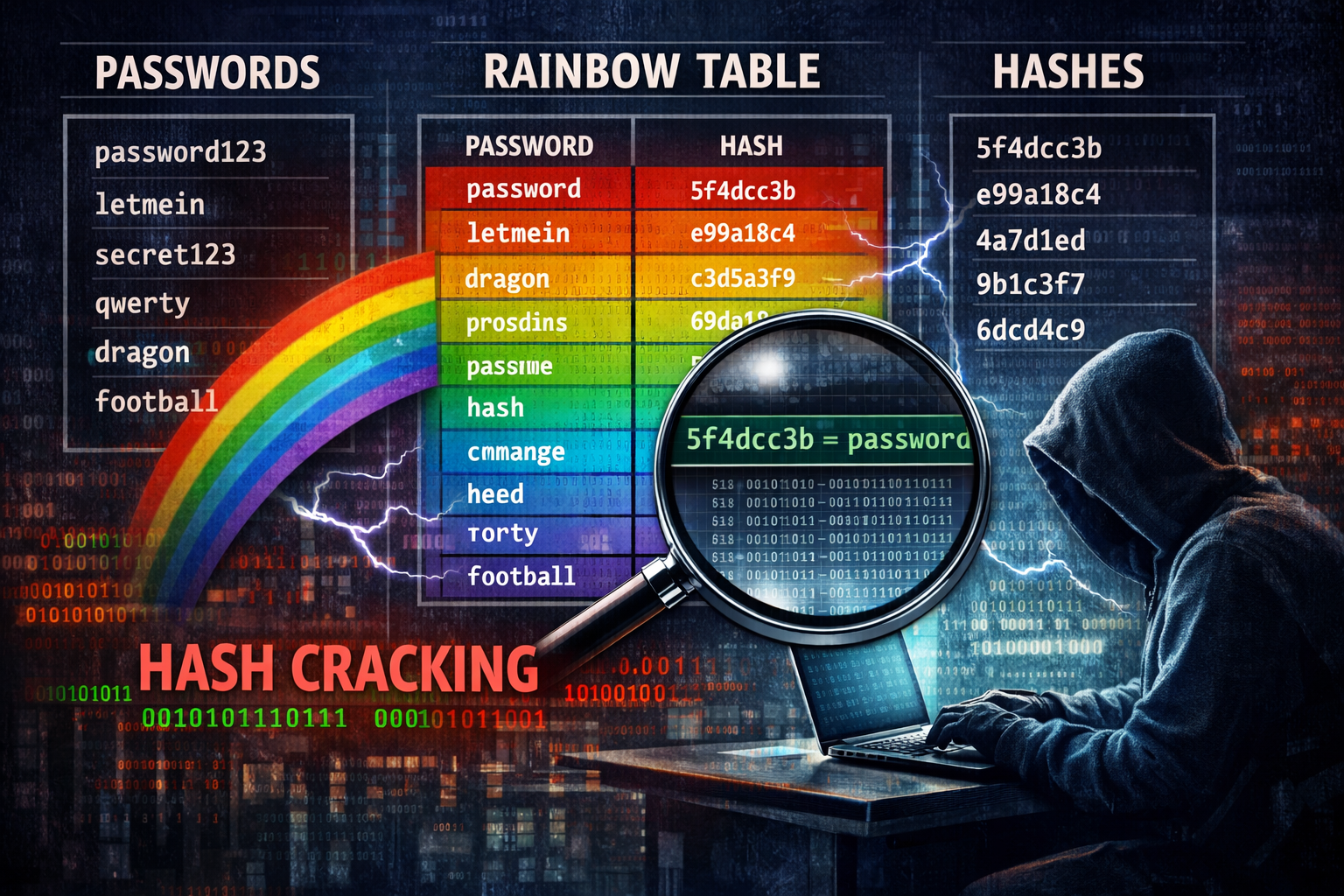
DISGOMOJI – Emoji-based Linux malware
Security researchers working for Volexity have discovered a novel malware which uses Emojis sent via a custom Discord server that has the ability to control compromised Linux distributions.
Volexity state that the malware seen is so far only focused on a specific Linux distro – BOSS – which is primarily used by Indian government agencies. They also believe that the malware is the work of a Pakistan threat actor known as UTA0137.
The malware could however be used to target any affected Linux distribution.
Custom Discord-C2
Volexity have identified that UTA0137 have modified a fork of the open-source discord-C2 server and use it as their Command-and-Control services using a set of Emojis for issuing commands to affected devices.
Initial compromise is achieved via backdoored decoy files, typically delivered as part of a phishing campaign. Once a victim device is compromised, a series of messages are sent to the device which allows threat actors to conduct various activities such as thake screenshots, upload more malware, download sensitive data, run arbitrary commands, and archive files for exfiltration at a later time.
In a sample analysed by Volexity, the researchers identified the initial compromise malware hidden within a backdoored pdf file which is used by Indian service personnel.

The malware is used to install a second stage from a remote server which is the DISGOMOJI malware. Thsi malware contains a hard-coded authentication token and server ID which the affected device uses to access the c2 server.
Once the victim device connects to the server, the threat actors can then interact with every victim individually using these discord channels.
The discord-c2 server is written in Golang (Go) and uses emojis to conduct a series of activities – The threat actors have forked this code and amended it to have greater capability.


On startup, DISGOMOJI sends a check-in message in the channel. This message contains information about the victim system, including:
- Internal IP
- Username
- Hostname
- Operating system
- Current working directory
The malware also downloads a script named uevent_seqnum.sh which is used to check if any USB devices are connected to the compromised device, and copy files from it devices to a local folder on the system so they can be retrieved later by attacker.
DirtyPipe
During their investigation, Volexity researchers uncovered UTA0137’s use of the DirtyPipe (CVE-2022-0847) privilege escalation exploit against Linux “BOSS 9” systems. A vulnerability which is over 2 years old.
This vulnerability concerns a flaw in the way the “flags” member of the new pipe buffer structure lacks proper initialization in copy_page_to_iter_pipe and push_pipe functions in the Linux kernel and could thus contain stale values.
An unprivileged local user could use this flaw to write to pages in the page cache backed by read only files and as such escalate their privileges on the system.
BOSS Linux
BOSS (Bharat Operating System Solutions) GNU/Linux was developed by C-DAC (Centre for Development of Advanced Computing) for enhancing the use of Free/ Open Source Software throughout India. It was mainly created for clients in defence sector, but has been updated to provide services for other sectors such as the education sector.
The accessibility of BOSS Linux has a constructive impact on the digital divide in India as more people now have access to software in their local language to use the Internet and other information and communications technology facilities.
C-DAC is the premier R&D organization of the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) for carrying out R&D in IT, Electronics and associated areas.