(26/09/23) Blog 269 – Yet another crypto exchange gets hacked
As the title of this post states, another crypto-currency exchange has been hacked, this time with the loss of approximately $200M USD.
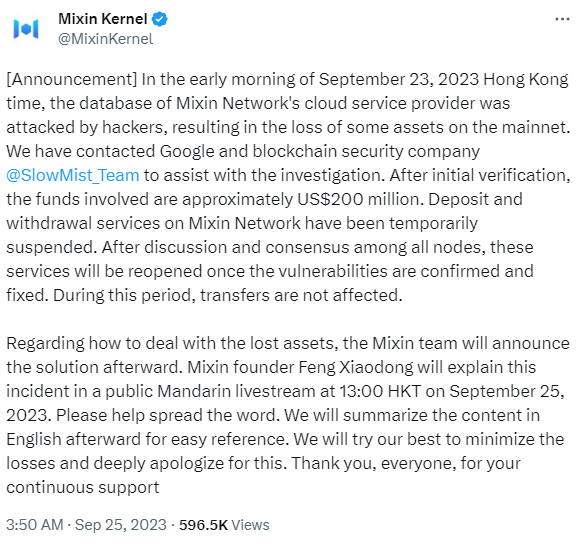
Early yesterday morning (25th), The Mixin exchange posted on twitter that in the early hours of the 23rd, the cloud provider used by the exchange was breached with the the loss of $200M and that as a result, all deposit and withdrawal services have been suspended.
Not the 1st exchange to be hit
Mixin is not alone in being the target of cyber-heist in 2023.
In Q1 of this year, 57 cryptocurrency thefts occurred, and since then a number of very large-profile attacks have happened. In august alone $45.8M worth of crypto was stolen in various attacks.
To date (not including the Mixin loss), there has been almost $1B worth of cryptocurrency stolen in 2023. The Mixin loss will tip that over the $1B amount.
Different types of Crypto losses
The world of crypto is as complex as that of FIAT currency with the different array of transaction types, trading platforms, exchange systems, etc. So it comes as no surprise that there are a wealth of different attacks that can occur leading to some huge losses.
Exit Scams
In the world of cryptocurrency, an exit scam is when promoters of a new cryptocurrency disappear with investors’ money during or after an initial coin offering (ICO).
The process involves promoters launching a new crypto platform, marketing the currency and concept, raising money from investors, possibly running the business for a short time, and then disappearing with the money and abandoning the project.
In 2023 so far, exit scams have cost the crypto world over $137M in losses
Flash loan attacks
With a traditional loan, a borrower typically has to put up some form of collateral in order to ensure that if the borrower cannot pay back the loan, the lender is still able to get their money back. Even if you have a good credit score, theirs no guarantee a lender will still offer a loan, but if you have collateral, such as property, then they might offer the loan and use the value in the property as the assurance that they have a means of recouping any money if the event of a default on the loan. This type of loan is often referred to as a secured loan.
There are also more risky loans called unsecured loans, where no collateral is required. In the world of crypto, these are called flash loans. This lack of collateral does not mean that the flash loan lender will not get their money back if the borrower has insufficient funds. It means that it will just be sent back in a different way. Instead of offering collateral, the borrower has to pay back the money right away.
A flash loan transaction is instantaneous and the smart contract for the loan must be fulfilled in the same transaction which is lent out. This means that the borrower has to call on other smart contracts in order to perform instant trades with the loaned capital, before the transaction itself ends. This process typically takes only a few seconds to complete.
Arbitrage is the most popular use case of a flash loan as it allows traders to earn profit from the price differences across various crypto exchanges. As an example, if LINK is trading at $30 on Exchange A and $35 on Exchange B, a user can borrow (via a flash loan) and conduct a separate order to buy 100 LINK for $3,000 at Exchange A, then sell them all for $3,500 at Exchange B and immediately pay back the $3,000 flash loan. In this scenario, the user will be able to profit $500 minus transaction fees.
A flash loan attack is a type of crypto attack where a thief takes out a flash loan from a lending platform and uses it in conjunction with market manipulation tactics in their favour. If done in huge sums, it can cause a particular crypto currency to loose a huge amount of value.
An excellent example of this type of attack occurred in 2021 against the platform PancakeBunny, which suffered an exploit that caused its token to plummet by more than 95% of its previous value.
The attacker in this incident initially borrowed a large amount of crypto through PancakeSwap and used it to manipulate the price of USDT/BNB and BUNNY/BNB in PancakeBunny’s trading pools.
This allowed the hacker to steal a large amount of BUNNY, which they then dumped on the market, causing the price to crash. The hacker then paid back the debt via PancakeSwap.
Data from trading platforms suggest that the attacker was able to get away with nearly $3 million in profits, leaving a tarnished protocol in their wake.
So far in 2023, Flash loan attacks have netted criminals approximately $261M in profits.
General exploitation of IT
As with most IT systems, general attacks on vulnerable systems are a major cause of losses. In 2023, the loss of $596M can be attributed to general exploitation of IT systems. This figure will now be increased by $200M with the Mixin attack, taking it to the largest type of attack against crypto in 2023.
Links to North Korea
Although many criminals abuse cryptocurrency systems on a frequent basis, there is one threat actor who has become the most adept at large scale attacks – North Korea.
Hackers working for the North Korean regime are by far the most adept at conducting crypto currency heists. At the moment, it is unknown who is behind the Mixin attack, but the attack is definately something the North Koreans are very good at conducting.
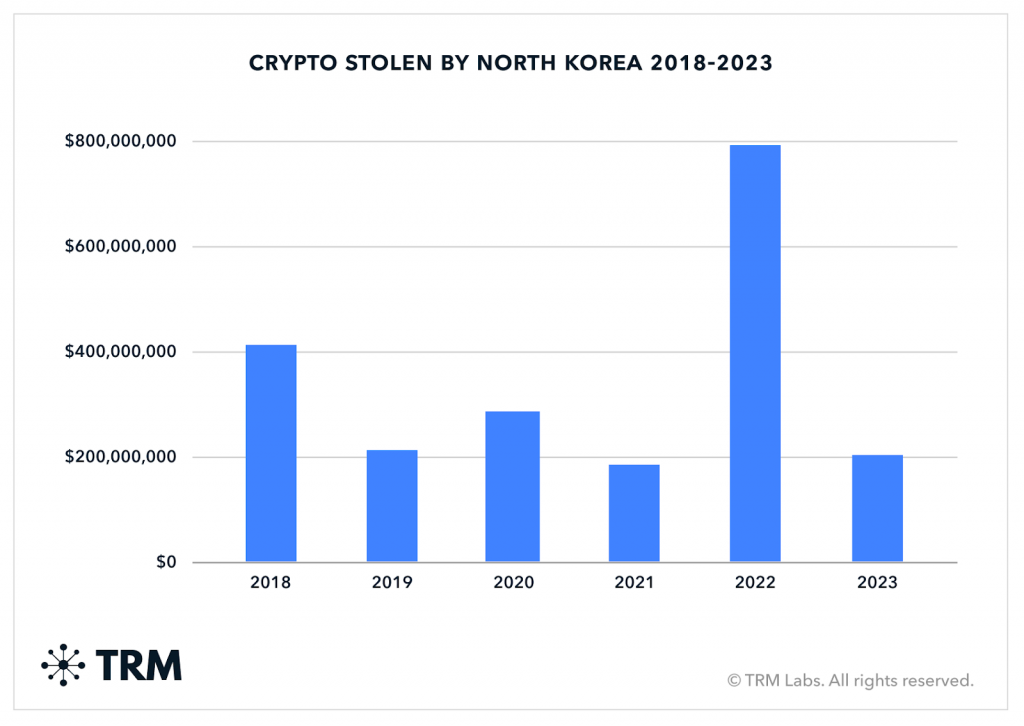
In 2022, North Korean attackers stole an estimated $1.7B in various crypto currencies. The Lazarus group is the most prolific of the North Korean hacking gangs
A report released in August by TRM states that in 2023, North Korean attackers have conducted more than 30 heists with a total value gained of over $200M.
This value is much less than their haul in 2022, but is still 10 times greater than other attackers in this space.