(10/07/23) Blog 191 – Analysing attacks on financial services
The latest “State of the Internet” report by Content Delivery Network (CND) provider Akamai focuses on the wide ranging attacks directed at financial services worldwide. The report, which is called “Enemy at the gate” uses Akamai’s unrivaled position as the worlds leading content delivery provider to delve into the details of attack traffic across the entire world.
Overview of the report
Key findings in the report show that:
- The financial services industry consistently ranks in the top three targeted verticals for web application and API, zero-day, and DDoS attacks.
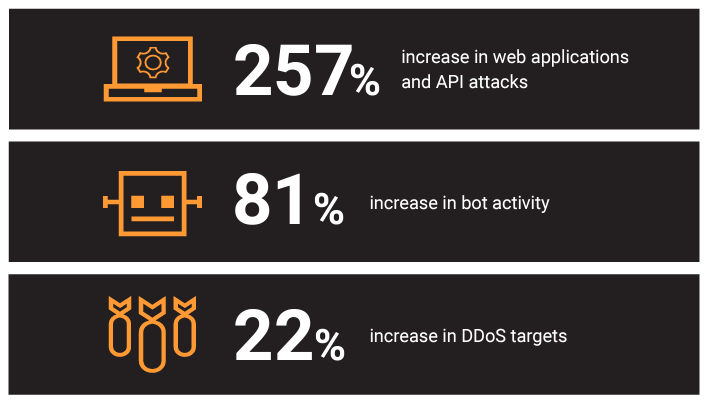
- FinServ showed a 3.5x surge in web application and API attacks year over year, the highest growth of any major industry.
- Within 24 hours, the exploitation of newly discovered zero-day vulnerabilities against FinServ can reach multiple thousands of attacks per hour and peak quickly, affording little time to patch and react.
- A significant increase in Local File Inclusion (LFI) and Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) attacks demonstrates how attackers are shifting toward remote code execution (RCE) attempts that present a larger strain on the internal security network.
- Abuse of FinServ customers is rampant, with more than 80% of FinServ attackers focusing on customer accounts rather than the organizations themselves, either directly or via phishing-related activities.
- Phishing campaigns (like Kr3pto) are introducing techniques that bypass two-factor authentication (2FA) solutions using one-time password tokens or push notifications.
Biggest threats
According to the report, the most concerning issue is the staggering surge in web application and API attacks — a 3.5x growth in the number of attacks against financial services, and the largest year-over-year increase of attacks in any sector with the exception of the gambling sector.
The Financial Services sector has seen consistent attack growth in targeted or focused attacks with a growing risk of web application attacks against organizations.
Research conducted by Positive Technologies showed breach of personal data, such as user ID and user credentials, happened at 91% of web apps; As such, it is imperative to secure web apps to prevent vulnerabilities being used as an entry point to breach target organisations.
Akamai research also found web apps and API vectors being commonly used by ransomware groups to gain initial access via the exploitation of vulnerabilities.
Bot Activity increase
Bot activity against financial services and their customers increased by 81%, and bots played a major role in account takeover accounts.
Threat actors often use bots to perform credential stuffing which involves the automated process of trying thousands of combinations of usernames and passwords in an attempt to achieve account takeovers.
These credentials used are often stolen from data breaches on other organisations, as criminals know that many people often re-use credentials from one account to another.
Bots are also used to conduct web scraping which allows criminals to extract data stored in legitimate websites to then accurately create phishing kits, which mimic the websites of target organisations, in order to scam customers.
In their research, Akamai found that 80.7% of phishing attacks in the FinServe sector were against regular customers, with the remaining 19.3% being against business account users.
DDoS attacks up by 22%
DDoS attacks figured prominently in attacks against financial institutions primarily during the beginning of the conflict between Russia and Ukraine.
Before the onset of the physical war in March 2022, it appears that a “cyber war” transpired first with both sides launching a slew of DDoS attacks in February 2022 to take down government and bank sites, disrupt the normal lives of citizens, and inflict damage.
Recently, pro-Russian attack groups REvil, Killnet, DDoS Empire, and RootSploit have specifically identified financial services as their target.
Reports emerged on the rising number of DDoS attacks against UK financial firms and other cyberattacks against Western European countries that expressed support for Ukraine.
Customers targeted
In addition to the financial institutions being targets for cyber threat actors, the customers of those organisations have also been in the sights of the attackers.
Five key categories of attacks are those aimed at FinServ customers:
- Account takeover – An attack whereby cybercriminals take ownership of online accounts using stolen passwords and usernames
- Web scrapers – Automated tools used to harvest information, such as website format and content from web pages, in a systematic fashion; often used for the purpose of replicating websites for the use of phishing attacks and scams
- Scanning tools – Tools used to scan web applications for vulnerabilities during the reconnaissance phase of an attack
- Denial-of-Service attackers – Web clients or botnets that use automated tools to launch volumetric DoS attacks
- Web attackers – Web clients or actors who perform generic web-oriented attacks such as SQLi, remote file inclusion (RFI), or XSS

Kr3pto toolkit most widely used
The Kr3pto toolkit was the one most frequently used and was associated with more than 500 domains.
The actor behind Kr3pto is a developer who builds and sells unique kits that target financial institutions and other brands. In some cases, these kits target financial firms in the United Kingdom and have the capability of bypassing 2FA.
The evidence also shows that this phishing kit, which was initially created more than three years ago, remains highly effective, and is still actively being used in the wild.