(09-03-23) Blog 68 – The Dark web – what is it exactly? Pt4
For this 4th and final installment in this mini-series, I will take a look at the ZeroNet system.
What is ZeroNet?
ZeroNet is an open-source, distributed, peer-to-peer web hosting service which has been available since 2015.
When accessing a Zeronet hosted website, the entire content of the site is downloaded to the visitor, including any non-browsed pages. The visitor then acts as a server for others in the network to access the content.
Due to this peer-to-peer approach of hosting content, there is no way to take down a ZeroNet page which still has people seeding the site, thus making such pages immune to third-party methods of taking them down, including DMCA takedown notices which tends to mean that there is a lot of pirated material hosted in the ZeroNet network.

So how does it work?
To use the ZeroNet network, you first need to install the ZeronNet service which is obtained from zeronet.io
Once installed, the service will run as a local webserver on your loopback IP address on port 43110.

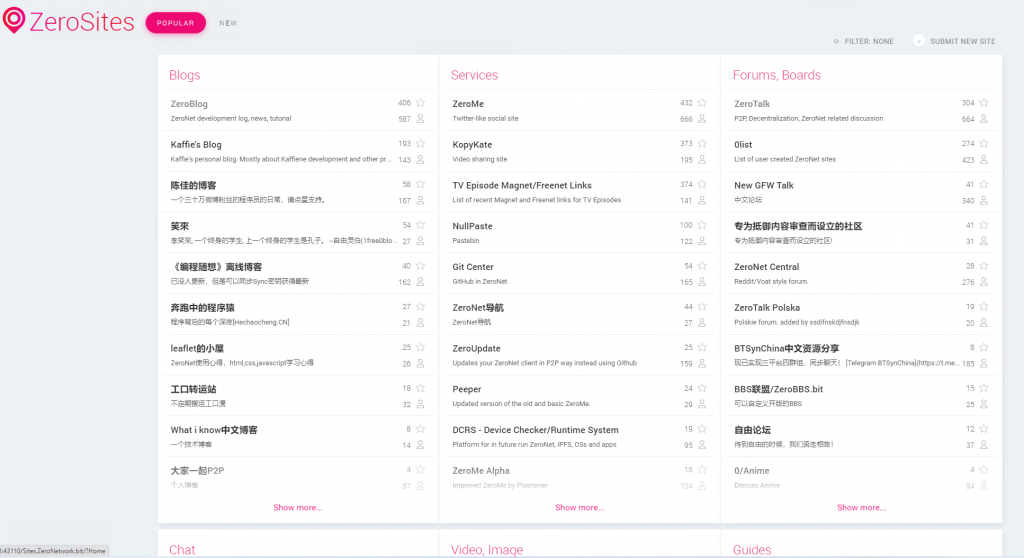
ZeroNet hosted websites can be accessed through an ordinary web browser such as Chrome or FireFox when using the ZeroNet application. The application also acts as the local webhost for any downloaded pages you visit.
The fact that you download any websites visited in their entirety also means that if your network goes offline, you can still browse the copies you are hosting until your network connection returns.
Websites hosted within ZeroNet are identified by a public key (specifically a namecoin .BIT address) instead of a traditional domain name / IP address.
An example of a ZeroNet website address would be something like https://talk.zeronetwork.bit.
The ZeroNet application uses a service called ncdns (Namecoin to DNS) to resolve the .bit url to the associated namecoin public key.
One your device has the public key, your browser then sends a request for IP addresses of devices currently sharing the content associated with that public key to a decentralised tracker service. This service is the same as that which is used in the BitTorrent network.
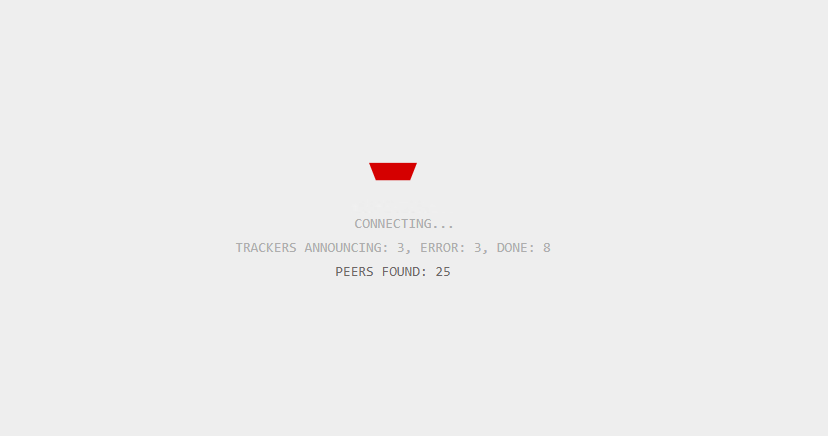
The tracker keeps a list of IP addresses currently hosting the site you are looking for, and responds with the list, whilst also registering your IP address as a visitor.
Upon receipt of the tracker list, your device connects to a number of the IP addresses listed and retrieves a file called content.json. This file holds the meta-data for the sites content, and the cryptographic signature of the sites owner.
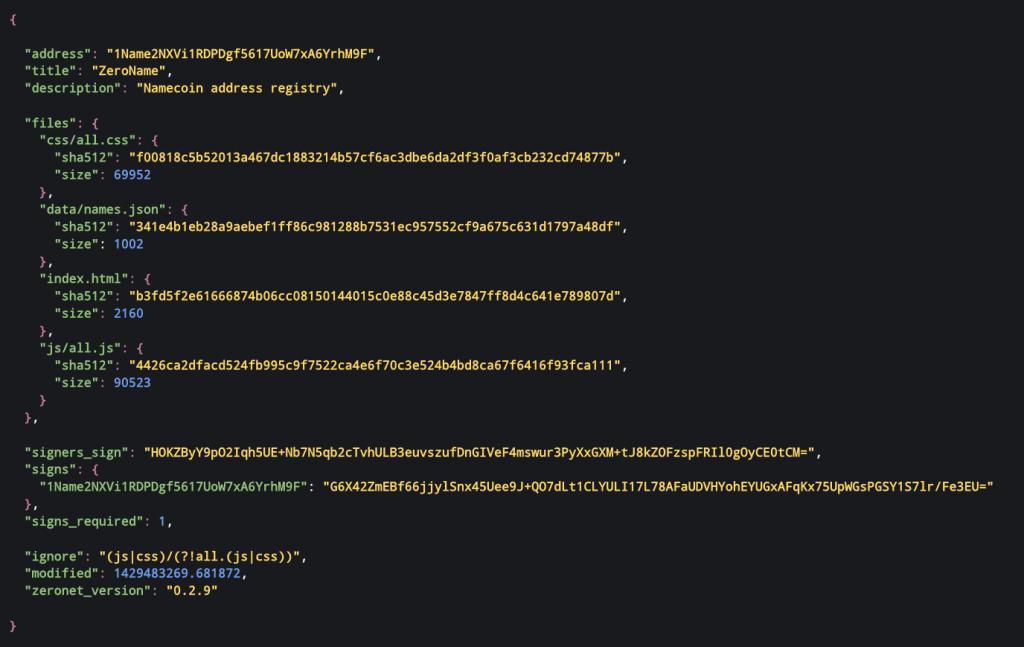
This signature is used with the websites namecoin address to verify the legitimacy of the content.json file, and as such the list of contents it holds.
After the verification process has completed, the browser then makes requests for the content of the website as identified in the content.json file.
All associated files downloaded are verified via the same process as described above.
Website security
When a site owner makes any changes to the content of the site, the private key for the website allows the owner to sign and publish any changes to the site content thus stopping others who are sharing the site from making unauthorised changes. Changes then propagate through the network and automatically update any copied versions.
This approach to website updates means that it is impossible for malicious threat actors to compromise sites with malware, unless they somehow have managed to compromise the site owners private key first.
If the site offers goods and services for sale, the transactions take place with the same namecoin identity as that which is used for the site itself, thus eliminating any chance of payments being hijacked, etc. The owner of the site, owns the namecoin wallet and as such any payments go straight to their wallet.
ZeroNet is not designed to be anonymous by default, but it does support the routing traffic through the Tor network for those which require the levels of anonymity it offers.
There are future plans to also enable I2P users the ability to access ZeroNet sites.